前面分析了ngx_array_t数组,现在看一下ngx_queue队列和ngx_hash哈希表的实现。
ngx_queue队列
ngx_queue_t是一个双向链表,实现了一个队列的操作逻辑。但是它的结构只行指针的操作,因而在定义自己的节点时,需要自己定义数据结构和分配空间,并包含一个ngx_queue_t类型的成员。
typedef struct ngx_queue_s ngx_queue_t;
struct ngx_queue_s {
ngx_queue_t *prev;
ngx_queue_t *next;
};
这和Linux内核的数据结构很像。它们都将链表节点塞入数据结构。Linux内核的链表这样定义:
struct list_head
{
struct list_head *next;
struct list_head *prev;
}
使用的时候
struct fox
{
unsigned long tail_length;
unsigned long weight;
bool is_fantastic;
struct list_head list;
}
结构如图所示:
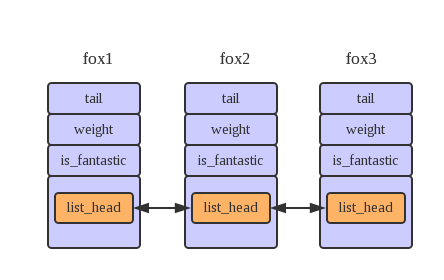
所以它用fox.list.next指向下一个节点,用fox.list.prev指向上一个节点。那我们如何从list_head找到fox的地址呢。内核提供了一个container_of()宏可以从链表指针找到父结构中包含的任何变量。
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr);\
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );)
而在Nginx也是效仿采用一样的宏获取父结构地址。
#define ngx_queue_data(q, type, link) \
(type *) ((u_char *) q - offsetof(type, link))
##用法
它的API定义了初始化,插入,排序,找中位节点等一系列操作。
用法如下:
typedef struct yahoo_s {
ngx_queue_t queue;
} yahoo_t;
typedef struct yahoo_guy_s {
ngx_uint_t id;
u_char* name;
ngx_queue_t queue;
} yahoo_guy_t;
ngx_int_t yahoo_no_cmp(const ngx_queue_t* p, const ngx_queue_t* n)
{
yahoo_guy_t *pre, *next;
pre = (yahoo_guy_t*) ngx_queue_data(p, yahoo_guy_t, queue);
next = (yahoo_guy_t*) ngx_queue_data(n, yahoo_guy_t, queue);
return ((pre->id > next->id) ? 1:0);
}
int main()
{
ngx_pool_t* pool;
yahoo_guy_t* guy;
ngx_queue_t* q;
yahoo_t* yahoo;
pool= ngx_create_pool(1024*10, NULL); //初始化内存池
int i;
// 构建队列
const ngx_str_tnames[] = {
ngx_string("rainx"), ngx_string("xiaozhe"), ngx_string("zhoujian")} ;
const in ids[] = {4611, 8322, 6111};
yahoo = ngx_palloc(pool, sizeof(yahoo_t));
ngx_queue_init(&yahoo->queue); //初始化queue
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
guy = (yahoo_guy_t*) ngx_palloc(pool, sizeof(yahoo_guy_t));
guy->id = ids[i];
guy->name = (u_char*) ngx_pstrdup(pool, (ngx_str_t*) &(names[i]) );
ngx_queue_init(&guy->queue);
// 从头部进入队列
ngx_queue_insert_head(&yahoo->queue, &guy->queue);
}
// 从尾部遍历输出
for(q = ngx_queue_last(&yahoo->queue);
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(&yahoo->queue);
q = ngx_queue_prev(q) ) {
guy = ngx_queue_data(q, yahoo_guy_t, queue);
printf("No. %d guy in yahoo is %s \n", guy->id, guy->name);
}
// 排序从头部输出
ngx_queue_sort(&yahoo->queue, yahoo_no_cmp);
printf("sorting....\n");
for(q = ngx_queue_prev(&yahoo->queue);
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(&yahoo->queue);
q = ngx_queue_last(q) ) {
guy = ngx_queue_data(q, yahoo_guy_t, queue);
printf("No. %d guy in yahoo is %s \n", guy->id, guy->name);
}
ngx_destroy_pool(pool);
return 0;
}
ngx_hash哈希表
ngx_hash表所用的hash算法为分桶后线性查找法,因而查找效率同key-value对成反比。对于常用的解决冲突的方法有线性探测、二次探测和开链法等。这里使用的是最常用的开链法(也是STL中使用的方法)。
哈希表整个结构如图所示:
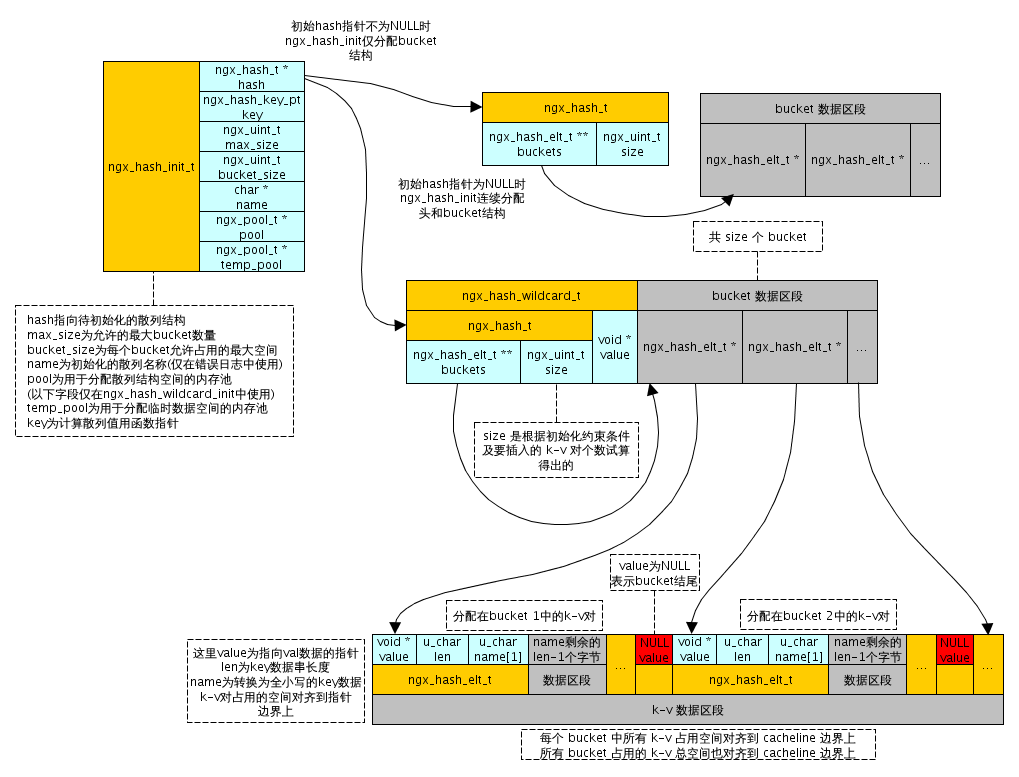
哈希表用下列数据结构进行管理
typedef struct {
ngx_hash_t *hash;
ngx_hash_key_pt key;
ngx_uint_t max_size;
ngx_uint_t bucket_size;
char *name;
ngx_pool_t *pool;
ngx_pool_t *temp_pool;
} ngx_hash_init_t;
在使用过程中,先会用ngx_hash_init_t实例化(类似于OOP思想,和内核驱动的用法相同)一个hash_init。
然后对这个“对象”赋值。
hash = (ngx_hash_t*)ngx_pcalloc(pool, sizeof(hash));
hash_init.hash = hash; // hash结构
hash_init.key = &ngx_hash_key_lc; // hash算法函数
hash_init.max_size = 1024*10; // max_size
hash_init.bucket_size = 64; //桶的大小
hash_init.name = "yahoo_guy_hash";
hash_init.pool = pool; // 用到的内存池
hash_init.temp_pool = NULL;
第一行分配了ngx_hash_t大小的内存存储如下hash结构。
typedef struct {
ngx_hash_elt_t **buckets;
ngx_uint_t size;
} ngx_hash_t;
然后创建一个需要加到hash table中的数组。
ngx_hash_key_t* arr_node; //存储键值对+hash值
elements = ngx_array_create(pool, 32, sizeof(ngx_hash_key_t));
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
arr_node = (ngx_hash_key_t*) ngx_array_push(elements);
arr_node->key = (names[i]);
arr_node->key_hash = ngx_hash_key_lc(arr_node->key.data, \
arr_node->key.len);
arr_node->value = (void*)descs[i];
}
ngx_hash_init(&hash_init, (ngx_hash_key_t*) elements->elts, \
elements->nelts)
最后将elements数组放到hash_init结构中,即将数组以hash table形式存储。
这就是整个hash结构的存储过程,查找相对简单,这里不再详述。
##参考 Linux Kernel Development. Page71~72