Redis是一种NoSQL的基于内存的key-value数据库。数据存储在内存和硬盘上,Redis周期性把更新数据写入磁盘,把修改操作写入追加记录文件中。
很巧的是,知乎的日志系统kids pub/sub pattern is ported from Redis。另外,强烈推荐Redis设计与实现,图文并貌,讲解清楚。另,另外,Redis是典型的Server-client系统,看完_APUE_之后看单机数据库的实现理解会更加深刻。
安装配置
- 在官网下载源码。
2.解压后进入目录make即可。
/src下的redis-server和redis-cli分别是服务器和客户端应用程序,可直接调用。运行命令到用户bin目录下方便调用:
cp src/redis-* /usr/local/bin
服务器运行界面如下:
客户端运行如下:
数据类型
Redis一共有五种数据类型:string,hash,list,set,zset。
string由sds.h/sds.c表示:
typedef char *sds;
//结构提定义,len为数组长度,free为空闲大小。
struct sdshdr {
unsigned int len;
unsigned int free;
char buf[];
};
//内存向高地址增长,s是字符数组实际位置。得到结构体首地址,然后运算符取得string大小。
static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s) {
struct sdshdr *sh = (void*)(s-(sizeof(struct sdshdr)));
return sh->len;
}
启动redis-server和redis-cli,在redis-cli中输入:
127.0.0.1:6379> SET book "Advanced Programming in the UNIX Environment"
可以将book的键值设为string类型。
127.0.0.1:6379> GET book
"Advanced Programming in the UNIX Environment"
list由adlist.h/adlist.c表示:
//可见list是一个双向链表
typedef struct listNode {
struct listNode *prev;
struct listNode *next;
void *value;
} listNode;
//遍历迭代器
typedef struct listIter {
listNode *next;
int direction;
} listIter;
//定义一个head和tail,把list放在中间。
typedef struct list {
listNode *head;
listNode *tail;
//典型的函数指针,同OOP成员函数
void *(*dup)(void *ptr);
void (*free)(void *ptr);
int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);
unsigned long len;
} list;
match采用遍历,算法复杂度为0(n)。对比LRU缓存机制应用hashmap的0(1)算法。
在redis-cli中输入:
127.0.0.1:6379> RPUSH brands Apple Microsoft Google
即可为brands设置list类型的键值。
127.0.0.1:6379> Lpop brands
"Apple"
hash由dict.h/dict.c表示:
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
typedef struct dictType {
unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2];
long rehashidx;
int iterators;
} dict;
这么复杂的数据结构借助一张图可以清晰的捋清楚。
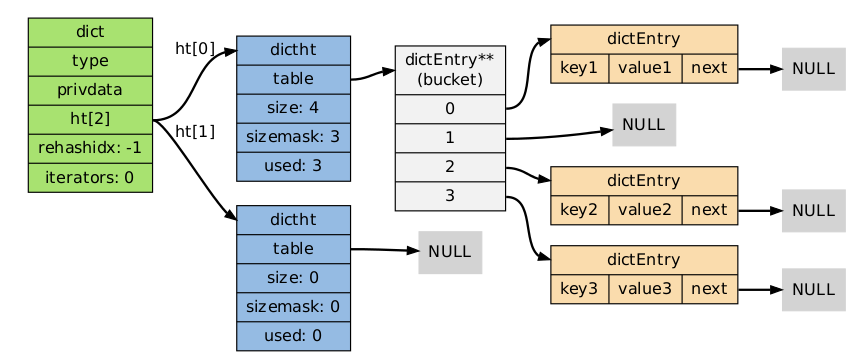
在redis-cli中输入:
127.0.0.1:6379> HSET cookbook type "source code analysis"
127.0.0.1:6379> HSET cookbook name "The design and implementation of Redis"
127.0.0.1:6379> HSET cookbook release-date "2013.3.8"
127.0.0.1:6379> HGETALL cookbook
1) "type"
2) "source code analysis"
3) "name"
4) "The design and implementation of Redis"
5) "release-date"
6) "2013.3.8"
hash类型键值的底层实现是hash表,hash表的常用寻址算法举例参见[3]。
Reference
[1].http://my.oschina.net/lvyi/blog/361141
[2].http://redisbook.readthedocs.org/en/latest/internal/redis.html
[3].http://my.oschina.net/lvyi/blog/327314