基于QT的QTcpServer类实现简单的HTTP服务器Tinyhttpd。代码存放在Github。
QThread和QTimer设置
当子类化QThread时,构造函数在旧线程中执行,然而run()在新线程中执行。如果一个成员变量的访问来自两个函数,然后从两个不同的线程访问变量,需要检查这样做是否安全。
QTimer不能在一个线程里实例化,而在另一个线程start或者stop。采取的方法是:
QTimer* keep_alive_timer;
void Request::run()
{
keep_alive_timer = new QTimer();
if (s_keep_alive_enable)
{
keep_alive = s_keep_alive_default;
keep_alive_timeout = s_keep_alive_timeout * 1000;// the wait time
connect(keep_alive_timer,SIGNAL(timeout()),this,SLOT(onTimeout()));
keep_alive_timer->setSingleShot(true);
keep_alive_timer->setInterval(keep_alive_timeout);
keep_alive_timer->start();
}
socket = new QTcpSocket();
if (!socket->setSocketDescriptor(socketDescriptor))
return;
connect(socket, SIGNAL(readyRead()), this, SLOT(onReadyRead()),
Qt::DirectConnection);
connect(socket, SIGNAL(disconnected()), this, SLOT(onDisconnected()),
Qt::DirectConnection);
exec();
}
QT事件循环机制
在上面的run()之后有一个exec()函数,它会进入事件循环。
Qt的事件循环是异步的,当调用QApplication::exec()时,就进入了事件循环。该循环可以简化的描述为如下的代码:
while ( !app_exit_loop )
{
while( !postedEvents ) { processPostedEvents() }
while( !qwsEvnts ){ qwsProcessEvents(); }
while( !postedEvents ) { processPostedEvents() }
}
先处理Qt事件队列中的事件,直至为空。再处理系统消息队列中的消息,直至为空。在处理系统消息的时候会产生新的Qt事件,需要对其再次进行处理。
QT垃圾回收机制
在程序中有很多地方new了一个对象并没有delete,这样会不会造成内存泄漏呢。
在QT中不会,它实现了自己的GC机制。
所有继承自QObject类的类,如果在new的时候指定了父亲,那么它的清理是在父亲被delete的时候。如果一个程序中,所有的QObject类都指定了父亲,那么他们是会一级级的在最上面的父亲清理时被清理。我们需要显式释放的是那些没有父对象的孤立的指针对象。
千万不要在QT类的子类里写析构函数,不要问我为什么知道。今天已经调了一天了。
多端口监听实现
port的配置文件这么定义
[httpd]
port=1234|1235|1236|1237
读取配置
bool ok;
QString t_port = Settings::instance().value("httpd/port").toString();
QStringList port_list = t_port.split("|");
for(int i = 0; i < port_list.size(); i++)
{
int port = port_list[i].toInt(&ok,10);
startInstance(port);
}
return true;
注意listen(QHostAddress::Any, 1234)指监听任何连上1234端口的IP。
incomingConnection虚函数
它是一个虚函数,当服务器收到连接请求时,它被QTcpServer调用。它在底层创建一个QTcpSocket,设置socket描述符并把描述符加入内部的列表(内部可能用select进行数据异步读写)。当重载这个函数时,可以改变服务器收到连接请求时的行为,相当于实现了一个hook。这样就可以在这个函数里实现http服务器。
void Server::incomingConnection(int socketDescriptor)
{
//有新的连接时,代替默认的功能(新建socket)
Request * request = new Request(socketDescriptor);
request->start();
}
可见socket描述符传到了Request实例里,这个描述符可能是实现多client并发连接的关键。
Request类
Request是QThread的子类,它对每一个描述符新建一个线程来处理它,实质就是处理每个client的请求。Request类的核心是Request::run(),它还实现了incommingConnection新建socket的base功能,通过start()来进行调用。
void Request::run()
{
socket = new QTcpSocket();
//用socket描述符作为新socket的描述符
if (!socket->setSocketDescriptor(socketDescriptor))
return;
connect(socket, SIGNAL(readyRead()), this, SLOT(onReadyRead()),
Qt::DirectConnection);
exec();
}
这个函数里需要用socketDescriptor作为新QTcpSocket对象的描述符。
If you want to handle an incoming connection as a new QTcpSocket object in another thread you have to pass the socketDescriptor to the other thread and create the QTcpSocket object there and use its setSocketDescriptor() method.
注意这个函数的最后一行是exec(),会进入事件循环,ServerThread::run()中也有exec()函数。
当数据准备好可读的时候,内核select发出readyRead()信号触发onReadyRead()函数。这样看来,onReadyRead()是一脉相承下来最重要的函数。
onReadyRead函数
这个函数里开始解析client发过来的request数据,并构造封装response数据。
这里是用浏览器抓取的标准的Request Headers和Response Headers。
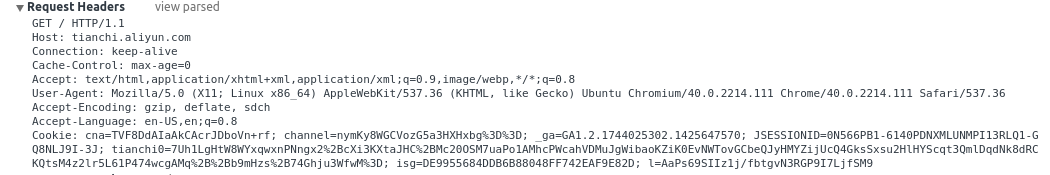

onReadyRead函数里的执行顺序如下:
-
getRequestHeader 负责读取request headers,确认client要求的是长\短连接。
-
tryResponseFile 返回请求路径的目录,有4种情况。ResponseDirectory()返回目录;直接返回页面;404;403
-
ResonseFile 调用response->response返回网页
-
clearStatus 如果是长连接,clearStatus()后继续socket监听。同时计时,如果超过timeout则删除socket连接。如果是短连接,直接删除socket连接。
状态记录
基于Redis的C官方客户端hiredis封装一个类Database,用来记录访问的数据。
安装hiredis
git clone https://github.com/antirez/hiredis.git && cd hiredis
make
sudo make install
sudo ldconfig
下面命令用来获取访问数据
redis-cli -p 6378
HMGET vistor:[n] time ip port agent
UI namespace
namespace Ui {
class MonitorUI;
}
class MonitorUI : public QMainWindow
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit MonitorUI(QWidget *parent = 0);
~MonitorUI();
private:
Ui::MonitorUI *ui;
};
前面声明了一个namespace Ui,它是一个匿名名称空间。该namespace 中的成员(变量或函数)具有独一无二的全局名称,避免名字碰撞 (name collisions)它的定义存在于自动生成的ui_monitorui.h文件中
namespace Ui {
class MonitorUI: public Ui_MonitorUI {};
}
因此Ui::MonitorUI和MonitorUI是不同的东西。
MonitorUI::MonitorUI(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::MonitorUI)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
}
可以看到ui是Ui::MonitorUI的一个实例。调用setupUi(this)。
setupUi() creates the actual instances of widgets for you. A form that you create in QtDesigner is stored just as XML file. So to be able to build the actual “window” with all the elements that you put on it in QtDesiner and display it in your application, setupUi() is created for you automatically by UIC (UI compiler - a Qt tool) so you don’t have to do that manually.
两个一样的类名用namespace来区分开,实现逻辑与显示的分离(类似MVC)。
总结
Singleton Pattern用在日志系统和配置系统中,这个例子中不是线程安全的。Singleton Pattern的实例具有和程序一样的生存期,因为instance是new出来的,它一直存在时。所以析构函数没有机会调用了。这里会产生memory leak。
Reference
[1].http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-27685749-id-3847998.html
[2].http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2011-03/33810p2.htm
[3].http://blog.csdn.net/envenler/article/details/8020064
[4].http://blog.csdn.net/jandunlab/article/details/14108595
[5].http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_a6fb6cc90101hohu.html
[6].http://qimo601.iteye.com/blog/1407911
[7].http://tuzhii.com/2015/03/19/dessignpattern/
[8].http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2496918/singleton-pattern-in-c
[9].http://blog.csdn.net/solstice/article/details/6186978